barfoed's test principle|Barfoed’s Test: Objective, Principle, Reagents, : Bacolod Barfoed’s test is a chemical test used for detecting the presence of monosaccharides. It is based on the reduction of cupric (II) acetate to cuprous (I) oxide (Cu 2 O), which forms a brick-red precipitate. Download Sea of Conquest: Pirate War Mod Apk 1.1.146 [No Ads] uploaded by slyvest. 5.0/5 38 47. Download APK (1445.28 MB) Use HappyMod to download Mod APK with 3x speed. Apps Mods More Apps Mods. Spotify: Music and Podcasts Mod Apk 8.10.9.722 [Unlocked] 76.59 MB. TikTok Mod Apk 36.2.5 [Unlocked][Premium] 277.88 MB. .
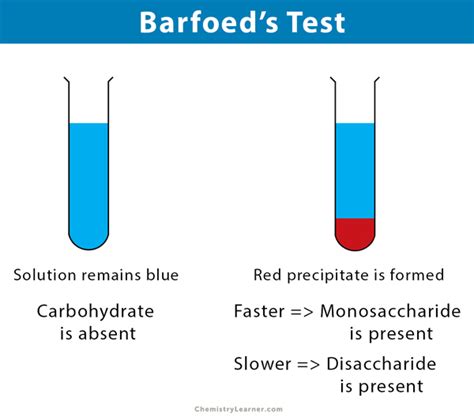
barfoed's test principle,The Barfoed reagent is made up of copper acetate in a dilute solution of acetic acid. Since acidic pH is unfavorable for reduction, . Tingnan ang higit paBarfoed’s test is a chemical test used to detect the presence of monosaccharides which detects reducing monosaccharides in the presence of disaccharides. This reaction can be used for disaccharides, but the reaction would be very slow. Tingnan ang higit pa
Image Reaction Source: Chemistry Learner, Created with BioRender.com. 1. The presence of red precipitate detects the presence of reducing monosaccharides in the sample. 2. If the color appears within the first few minutes, the sample contains reducing . Tingnan ang higit paBarfoed’s test is a chemical test used for detecting the presence of monosaccharides. It is based on the reduction of cupric (II) acetate to cuprous (I) oxide (Cu 2 O), which forms a brick-red precipitate.
Barfoed’s Test: Objective, Principle, Reagents, Barfoed’s test is a biochemical test used to detect monosaccharide (reducing) sugars in solution. The technique was devised by a Swedish physician C. . Principle. Barfoed’s test reaction is based on the reduction of cupric acetate by reducing monosaccharides and reducing disaccharides. Reduction of cupric .Barfoed's test is a chemical test used for detecting the presence of monosaccharides. It is based on the reduction of copper(II) acetate to copper(I) oxide (Cu2O), which forms a brick-red precipitate. RCHO + 2Cu + 2H2O → RCOOH + Cu2O↓ + 4H (Disaccharides may also react, but the reaction is much slower.) The aldehyd.
Barfoed’s test is a chemical test used to distinguish between monosaccharides and disacchar ides according to their capacity to generate copper(I) oxide (Cu 2 O) in an .
Principle of Barfoed’s test: Barfoed’s test is used for distinguishing monosaccharides from reducing disaccharides. Monosaccharides usually react in about 1-2 minute while the reducing .A biochemical test to detect monosaccharide (reducing) sugars in solution, devised by the Swedish physician C. T. Barfoed (1815–99). Barfoed's reagent, a mixture of ethanoic .

How to perform the test: One ml of a sample solution is placed in a test tube. Three ml of Barfoed's reagent (a solution of cupric acetate and acetic acid) is added. The solution is .
Barfoed’s test is based on the reaction of reducing sugars with copper acetate in a dilute acetic acid solution. The copper acetate acts as an oxidizing agent that accepts .Barfoed’s test: A chemical test known as the Barfoed's test is used to identify the presence of monosaccharides and can identify reducing monosaccharides when disaccharides are present. Disaccharides might be used in this reaction, although it would proceed extremely slowly. A diluted acetic acid solution of copper acetate Cu (CH 3 .
Barfoed’s test Principle: At the point, when barfoed’s reagent mixes with series of monosaccharide or disaccharide and warmed in bubbling water shower, they react and a precious stone . This is the video on barfoed's test which is done for the detection of monosaccharides along with live demonstrationSubscribe my channel from - http://www.y. Principle: Barfoed’s test is a simple and rapid test used for the identification of monosaccharides. In this test, a sample is heated with Barfoed’s reagent (a mixture of copper acetate and acetic acid) in a boiling water bath. Monosaccharides (such as glucose, fructose, and galactose) reduce the copper ions in the reagent to form a red .barfoed's test principlePrinciple. This test is based on the reaction of alpha-naphthol with carbohydrates in the presence of sulfuric acid. The sugars react with alpha-naphthol in an acidic environment to form purple-colored furfural or hydroxymethylfurfural derivatives. . Barfoed’s Test. It is a differentiating test to distinguish between monosaccharides and .A biochemical test to detect monosaccharide (reducing) sugars in solution, devised by the Swedish physician C. T. Barfoed (1815–99). Barfoed's reagent, a mixture of ethanoic (acetic) acid and copper (II) acetate, is added to the test solution and boiled. If any reducing sugars are present a red precipitate of copper (II) oxide is formed.barfoed's test principle Barfoed’s Test: Objective, Principle, Reagents, Barfoed’s test Barfoed’s test mainly used for detecting the presence of mono-saccharides or disaccharides in the given sample. Principle The reduction of cupric acetate by reducing monosaccharides and disaccharides is the base of Barfoed’s test reaction. Cupric acetate is reduced to cuprous oxide, which results in a brick red colour .

Barfoed’s test makes use of Barfoed’s solution, which contains copper acetate in the dilute acetic acid with a pH of 4.6. Principle: In Barfoed’s test, the reducing monosaccharide is oxidized by the copper ion in the solution to form a carboxylic acid and copper (I) oxide, which results in the formation of a red-coloured precipitate .
barfoed's test principle|Barfoed’s Test: Objective, Principle, Reagents,
PH0 · Carbohydrates
PH1 · Barfoed’s Test: Principle, Reagents & Result Interpretation
PH2 · Barfoed’s Test: Principle, Procedure, Reaction, and Result
PH3 · Barfoed’s Test: Objective, Principle, Reagents,
PH4 · Barfoed’s Test: Objective, Principle, Procedure, Results And
PH5 · Barfoed’s Test: Objective, Principle, Procedure, Results
PH6 · Barfoed’s Test
PH7 · Barfoed's test
PH8 · Barfoed's Test